Stacks Concept
A stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in first-out (LIFO) principle. In the pushdown stacks only two operations are allowed: push the item into the stack, and pop the item out of the stack. A stack is a limited access data structure - elements can be added and removed from the stack only at the top. push adds an item to the top of the stack, pop removes the item from the top. A helpful analogy is to think of a stack of books; you can remove only the top book, also you can add a new book on the top.A stack is a recursive data structure. Here is a structural definition of a Stack:
a stack is either empty or it consistes of a top and the rest which is a stack;
 Prefix, Infix, & Postfix
1. Prefix adalah notasi yang terbentuk atas
operator dengan operand, dimana oprator
didepan operand.
Contoh: A + B * C (infix).
maka notasi prefixnya adalah: +A*BC.
Pemecahannya:
Diketahui ada 3 operand yaitu: A, B, C dan 2
operand yaitu: +, *.proses dimulai dengan
melihat dari hirarkhi oprator.Contoh diatas operator yang tertinggi adalah * kemudian +. Tanda * diapit oleh 2 operand yaitu B*C, prefixnya dengan menggabungkan operand dan memindahkan operator ke depan dari operand,sehingga fungsi B*C, notasi prefixnya menjadi *BC, sehingga hasil sementara dari notasi prefix adalah A+*BC.
Selanjutnya mencari prefix untuk operator yang berikutnya yaitu +, cara yang dilakukan sama seperti diatas, operator + diapit oleh operand, yaitu A dan *BC, gabungkan operand,sehingga menjadi A*BC,lalu pindahkan operator kedepan operand,sehingga hasil akhir menjadi +A*BC.
2.Infix adalah notasi yang membentuk atas operator dengan operand,dimana operator berada diantara operand.
Contoh : - A + B * C
- (A + B) * C
- A - (B + C) * D ^ E
3.Postfix adalah notasi yang membentuk atas operator dengan operand, dimana operator berada dibelakang operand.
Contoh : A + B * C (infix).
maka notasi postfix adalah ABC*+.
Pemecahannya:
Diketahui ada 3 operand yaitu : A,B,C dan 2 operator yaitu : +, *. proses dimulai dengan melihat dari hirarkhi operator.Contoh diatas operator yang tertinggi adalah * kemudian +.
Tanda * diapit oleh kedua operand yaitu B dan C yaitu B*C, postfix dengan menggabungkan operand B dan C menjadi BC,lalu memindahkan operator ke belakang operand C, sehingga fungsi B*C, notasi postfixnya menjadi BC*.Sehingga hasil sementara dari notasi postfix adalah A + BC*.
Selanjutnya mencari postfix untuk operator yang berikutnya, yaitu +, dengan cara yang dilakukan sama seperti di atas, operator + diapit oleh 2 operand, yaitu A dan BC*. Gabungkan operand tersebut, sehingga menjadi ABC*, lalu pindahkan operator + kebelakang operand ABC*.
Sehingga hasil akhir menjadi ABC*+.
Stack Applications
Stacks are widely used to:
• Reverse
the order of data
• Convert
infix expression into postfix
• Convert
postfix expression into infix
• Backtracking
problem
• System
stack is used in every recursive function
• Converting
a decimal number into its binary equivalent
Queue Concept
A Queue is a linear structure which follows
particular order in which the operations are performed. The order is First In First Out (FIFO). A good example of a queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first. The difference between stacks and queues is in removing. In a stack we remove the item the most recently added; in a queue, we remove the item the least recently added. 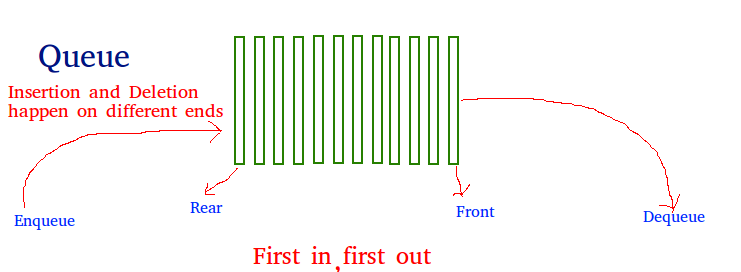
Circular Queue
Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called ‘Ring Buffer’.

In a normal Queue, we can insert elements until queue becomes full. But once queue becomes full, we can not insert the next element even if there is a space in front of queue.
Priority Queue
Priority Queue is an extension of queue with following properties.
That is my summary for Data Structure Session 4 on 2nd March 2020, Thank you
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~adamchik/15-121/lectures/Stacks%20and%20Queues/Stacks%20and%20Queues.html
http://risasisteminformasi.blogspot.com/2013/02/notasi-prefixinfix-dan-postfix.html?m=1https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/queue-data-structure/ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/circular-queue-set-1-introduction-array-implementation/ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/priority-queue-set-1-introduction/ |
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar